Formula For Degree Of Unsaturation
Key TERMS
Make certain that y'all can ascertain, and use in context, the fundamental terms beneath.
- caste of unsaturation
- saturated
- unsaturated
In that location are many means one tin go about determining the structure of an unknown organic molecule. Although, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and infrared radiation (IR) are the primary ways of determining molecular structures, calculating the degrees of unsaturation is useful information since knowing the degrees of unsaturation brand it easier for one to effigy out the molecular structure; it helps one double-check the number of [latex] \pi [/latex] bonds and/or cyclic rings.
Saturated and Unsaturated Molecules
In the lab, saturation may be thought of as the point when a solution cannot dissolve anymore of a substance added to it. In terms of degrees of unsaturation, a molecule only containing single bonds with no rings is considered saturated.
Unlike saturated molecules, unsaturated molecules contain double bond(south), triple bail(s) and/or band(s).
| CHiiiCH=CHCH3 | 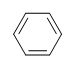 | 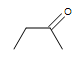 |  | 3-chloro-five-octyne |
Calculating The Degree of Unsaturation (DoU)
If the molecular formula is given, plug in the numbers into this formula:
\[ DoU= \dfrac{2C+2+Due north-X-H}{2} \tag{7.2.one}\]
- C is the number of carbons
- North is the number of nitrogens
- X is the number of halogens (F, Cl, Br, I)
- H is the number of hydrogens
As stated before, a saturated molecule contains only single bonds and no rings. Another way of interpreting this is that a saturated molecule has the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible to be an acyclic alkane. Thus, the number of hydrogens can be represented by 2C+2, which is the general molecular representation of an alkane. As an example, for the molecular formula C3H4 the number of bodily hydrogens needed for the chemical compound to be saturated is viii [2C+2=(2×3)+two=8]. The chemical compound needs four more than hydrogens in order to exist fully saturated (expected number of hydrogens-observed number of hydrogens=8-4=4). Degrees of unsaturation is equal to ii, or half the number of hydrogens the molecule needs to be classified every bit saturated. Hence, the DoB formula divides by 2. The formula subtracts the number of X'southward because a halogen (X) replaces a hydrogen in a compound. For instance, in chloroethane, C2H5Cl, at that place is ane less hydrogen compared to ethane, CtwoH6.
For a compound to be saturated, there is one more than hydrogen in a molecule when nitrogen is present. Therefore, nosotros add the number of nitrogens (Due north). This can exist seen with CthreeH9N compared to CiiiHeight. Oxygen and sulfur are not included in the formula because saturation is unaffected by these elements. As seen in alcohols, the same number of hydrogens in ethanol, C2H5OH, matches the number of hydrogens in ethane, C2Hvi.
The post-obit nautical chart illustrates the possible combinations of the number of double bond(s), triple bond(due south), and/or ring(south) for a given degree of unsaturation. Each row corresponds to a dissimilar combination.
- Ane degree of unsaturation is equivalent to i ring or i double bond (1 [latex] \pi [/latex] bail).
- Two degrees of unsaturation is equivalent to 2 double bonds, i band and 1 double bond, 2 rings, or i triple bond (two [latex] \pi [/latex] bonds).
| DoU | Possible combinations of rings/ bonds | ||
| # of rings | # of double bonds | # of triple bonds | |
| 1 | one | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | ii | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| i | 1 | 0 | |
Remember, the degrees of unsaturation only gives the sum of double bonds, triple bonds and/or rings. For instance, a degree of unsaturation of 3 tin contain 3 rings, ii rings+1 double bond, 1 ring+ii double bonds, 1 ring+1 triple bail, i double bond+1 triple bail,or 3 double bonds.
Example
Benzene
What is the Degree of Unsaturation for Benzene?
SOLUTION
References
- Vollhardt, K. P.C. & Shore, N. (2007). Organic Chemical science (vthEd.). New York: Westward. H. Freeman. (473-474)
- Shore, North. (2007). Study Guide and Solutions Transmission for Organic Chemistry (fivethursday Ed.). New York: West.H. Freeman. (201)
Examples
Issues
- Are the post-obit molecules saturated or unsaturated:
-
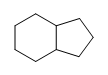 (b.)
(b.)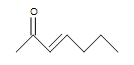 (c.)
(c.)  (d.) C10H6N4
(d.) C10H6N4
-
- Using the molecules from 1., give the degrees of unsaturation for each.
- Summate the degrees of unsaturation for the following molecular formulas:
- (a.) C9H20 (b.) CviiH8 (c.) C5H7Cl (d.) C9H9NO4
- Using the molecular formulas from 3, are the molecules unsaturated or saturated.
- Using the molecular formulas from 3, if the molecules are saturated, how many rings/double bonds/triple bonds are predicted?
- (d.) unsaturatedv.(a.) 0 (Remember-a saturated molecule only contains unmarried bonds)
(b.) The molecule tin contain any of these combinations (i) iv double bonds (ii) 4 rings (3) 2 double bonds+2 rings (iv) 1 double bond+3 rings (v) iii double bonds+ane ring (half dozen) 1 triple bond+2 rings (vii) ii triple bonds (8) 1 triple bond+i double bond+one ring (ix) 1 triple bond+ii double bonds
(c.) (i) 1 triple bond (ii) 1 ring+1 double bond (three) ii rings (iv) 2 double bonds
(d.) (i) 3 triple bonds (ii) ii triple bonds+2 double bonds (iii) ii triple bonds+1 double bond+1 ring (iv)… (Equally you tin see, the degrees of unsaturation only gives the sum of double bonds, triple bonds and/or ring. Thus, the formula may requite numerous possible structures for a given molecular formula.)
Answers
1.
2. If the molecular structure is given, the easiest way to solve is to count the number of double bonds, triple bonds and/or rings. However, you tin besides determine the molecular formula and solve for the degrees of unsaturation past using the formula.
3. Utilize the formula to solve
4.
Exercises
Questions
1.
Calculate degrees of unsaturation (DoU) for the post-obit, and propose a structure for each.
A – C5H8
B – C4H4
two.
Calculate the caste of unsaturation (DoU) for the following molecules
A – CfiveHfiveN
B – C5HfiveNO2
C – C5HvBr
iii.
The post-obit molecule is caffeine (C8H10NorthivOtwo), make up one's mind the degrees of unsaturation (DoU).

Solutions
1.
ii.
Evidence Reply
A = 4, B = 4, C = 3
3.
Formula For Degree Of Unsaturation,
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-mcc-organicchemistry/chapter/calculating-degree-of-unsaturation/
Posted by: marquezgraime.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Formula For Degree Of Unsaturation"
Post a Comment